Mensuration is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of different geometrical shapes, their perimeter, area , surface area, curved surface area, volume etc. Basically, there are two type of geometric shapes (i) 2D shapes (ii) 3D shapes
2D shapes are : circle, square, rectangle, square , parallelogram, rhombus etc.
3D shapes are : cube , cylinder, cone , cuboid, sphere , prism , pyramid , cone etc.
Now let’s learn all the important mensuration formulas involving 2D and 3D shapes. Using this mensuration formulas list, it will be easy to solve the mensuration problems.
Contents
Mensuration Formulas Chart
Mensuration formulas for 2D -shapes:
| Name | Figure | Area | Perimeter |
| Rectangle |  l= length, b=breadth l= length, b=breadth |
||
| Square |  a= side , d= diagonal a= side , d= diagonal |
If d is given , then |
4 x side= 4a |
| Triangle
(scalene) |
 b =base, h= height or altitude of a triangle |
(i) (ii) Heron’s Formula |
a+b+c |
| Equilateral triangle |  a= side , h= height or altitude a= side , h= height or altitude |
(i) (ii) |
3a |
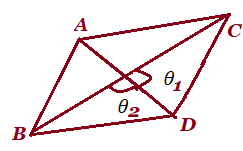
| Quadrilateral |  AC=diagonals AC=diagonals
|
(i)
(ii) |
AB+BC+CD+AD |
| Parallelogram |  a and b be the lengths of parallel sides and h be the height a and b be the lengths of parallel sides and h be the height |
(i)Area= base x height
(ii) area= |
2(a+b) |
| Rhombus |  a=each equal sides , a=each equal sides , |
4a | |
| Trapezium | 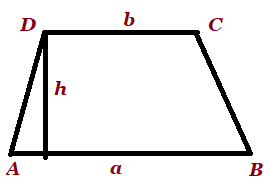 a, b are parallel sides a, b are parallel sides
h is the perpendicular distance between parallel sides |
AB+BC+CD+DA | |
| Circle |  r=radius , r=radius , |
circumference= |
|
| Semi-circle | 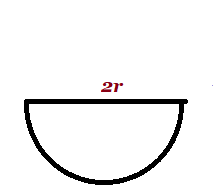 r =radius r =radius |
||
| Sector of a circle | 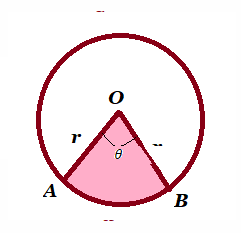 o centre , r= radius o centre , r= radius
l=length of arc AB, |
(i) (ii) |
l+2r |
| Regular hexagon | 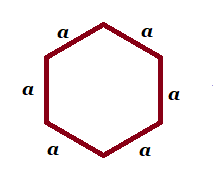 a= each of the equal side a= each of the equal side |
6a | |
| Regular octagon |  a= each of the equal side a= each of the equal side |
8a
|
Mensuration formulas for 3D -shapes:
| Name | Figure | Volume | Lateral /Curved surface area | Total surface Area |
| Cube | 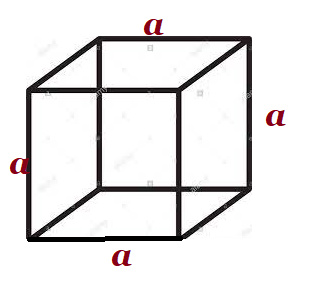 a=side/edge a=side/edge |
|||
| cuboid | 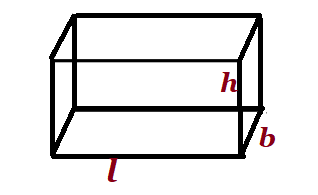 l=length, b=breadth, h=height l=length, b=breadth, h=height |
lbh | ||
| Right circular cylinder | 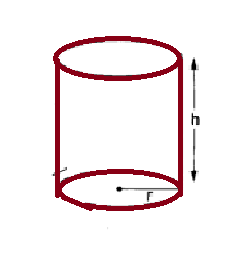 r= radius of base r= radius of base
h=height |
|||
| Right triangular prism |  |
area of base x height | perimeter of base x height | lateral surface area+2(area of base) |
| Sphere |  r=radius r=radius |
|||
| Hemisphere | 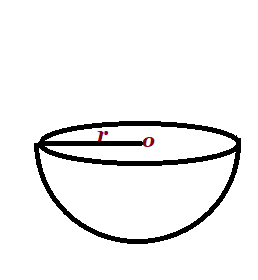 r= radius r= radius |
|||
| Pyramid | 
|
lateral surface area+base area | ||
| Cone | 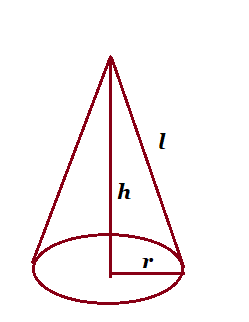 l=slant height, l=slant height,
|
|||
| Frustum of a cone |  |
lateral surface area+ |
Download PDF:
| Mensuration Formulas pdf |
You might also be interested in:
- Area of Triangles- Definition, Formula and Examples
- Trigonometric values| Trigonometric ratio table
- Algebra Formulas | List of all Algebraic Identities PDF download
- Circle| Circle formulas, Parts and Properties
- FREE RRB NTPC MATHEMATICS MOCK TEST