Definite Integration Involving Modulus Function
There is no anti-derivative for a modulus function; however we know it’s definition
Thus we can split up our integral in two parts. One part must be completely negative and the another must be completely positive. This strategy is known as splitting . To split correctly it is better to draw the modulus graph so that we can get the correct equation to represent each portion of the modulus graph .
Example 1. Find the value of
Sol. For a periodic function with period
,
, where
is any natural number.
Here whose period is
.
Hence
= ( since
)
= = 9 x 2 =18 .
Thus
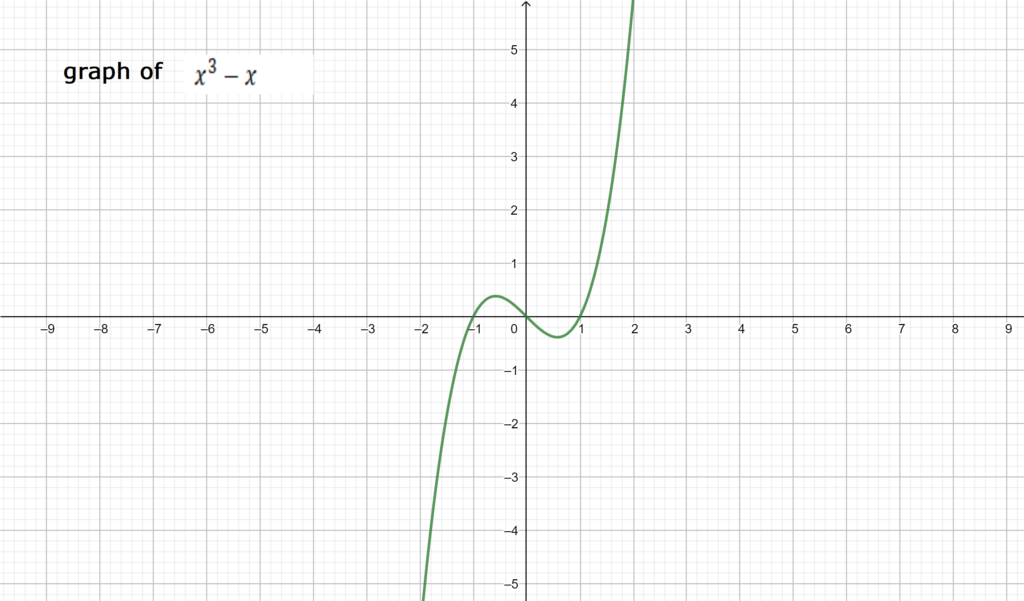
Example 2. Evaluate
Sol. We note that on
and
on
and that
on
.
Graph of
So
=
=
=
=
Example 3. Find the value
Sol. We know that and
has one common value at
. In the interval
,
and in
,
. Thus
in
and
in
.
So
=
=